Two options of biological sample preparation for transmission electron microscopy are available:
- Conventional TEM sample preparation (plastic embedding and ultramicrotomy)
- Cryo-TEM (cryofixation and operating the TEM at -170°C).
Conventional TEM sample preparation
The sample preparation is suitable for tissues and cell cultures, both adhering and non-adhering. The procedure is divided into two significant steps
- Fixation, dehydration and embedding in resin blocks
- The ultramicrotomy of resin blocks.
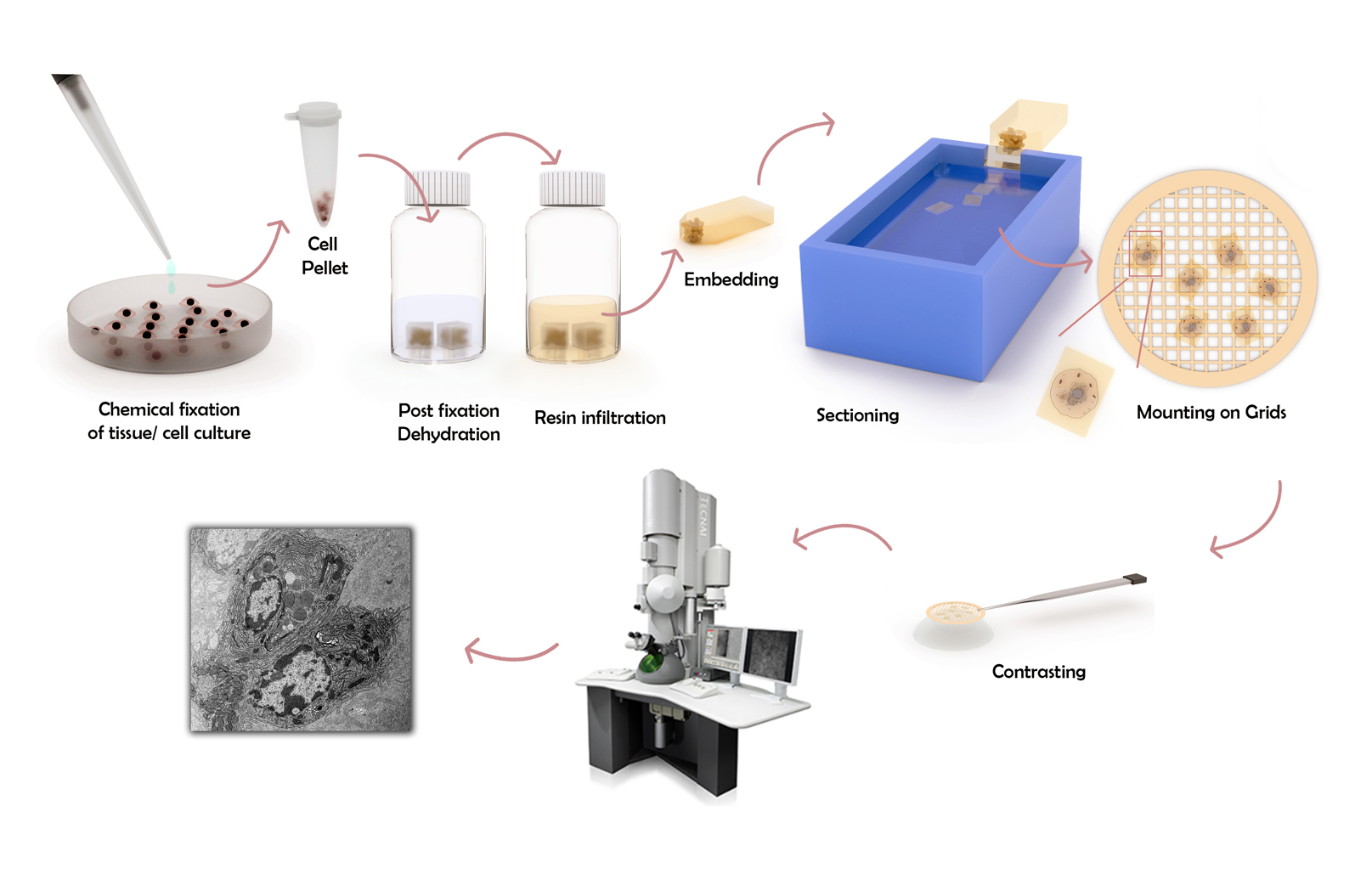
Fixation, dehydration and resin embedding
Modus operandi
The embedding of biological samples in plastic blocks is subdivided into three chapters:
- Fixation
- Dehydration
- Resin embedding, or polymerization
Pilot studies and proof-of-principle requests are generally accepted after initial discussions with users. Such pre-studies allow us to tweak existing protocols to demonstrate the feasibility of the techniques for the project. Once the protocol is adjusted and the results show the required potential, the project leader is informed, and a designated person attached to the project is trained. Importantly, this way, the scientist has complete control over their sample(s) and the treatment (both before and after fixation), which increases the accuracy of interpreting the results. This approach is designed to ensure cost efficiency, enhance accessibility to these techniques, and create a fair pooling of consumables.
The preparation of TEM samples is conducted at regular intervals. Note: safety protocol prohibits users from accessing the laboratory facilities. The SNFS-eligible cost for resin embedding of biological samples (includes fixation, dehydration, and polymerization) are outlined below.
SNSF-eligible cost breakdown
Scientific support: The preparation protocol requires an expert’s attention for 10 hours to be completed. A maximum of 10 samples can be processed in one batch (i.e., 1 or 10 samples equals the same costs).
Consumables: For each batch, 100 CHF is charged to cover the cost of consumables.
| Cost | Total | Total costs | |
| Scientific support | 40 CHF/h | 10 h | 400 CHF |
| Consumables | 100 CHF per batch | 1-10 samples | 100 CHF |
Summary and output
Summary: The biological resin embedding of up to 10 samples costs 400 CHF in scientific support and 100 CHF in consumables per batch.
Output: Cured resin blocks are ready for ultramicrotomy. Such blocks can be stored for extended periods, are not toxic, archived, and even revisited years later.
Ultramicrotomy of resin blocks
Modus operandi
Ultramicrotomy is performed in the ultramicrotomy lab of the section Medicine (Other direct costs of infrastructure use). If users have their own sample preparation station, they can prepare the cured resin blocks themselves. The cost for ultrathin sectioning is detailed below.
SNSF-eligible cost breakdown
Scientific support: The sectioning (trimming and ultramicrotomy) of one sample requires one hour.
Consumables: TEM grids are charged at CHF per grid. Typically, 2-3 grids are produced per sample.
| Hourly cost | Total | Total costs | |
| Scientific support | 40 CHF/h | 1 h/sample | 40 CHF/sample |
| Other direct costs of infras-tructure use | 15 CHF/h | 1 h/sample | 15 CHF/sample |
| Consum-ables | 2 CHF / grid | 2-3 grids/sample | 5 CHF/sample |
Summary and output
Summary: the costs amount to 60 CHF per resin block. Note: There is no guarantee that the ultramicrotomy will be successful. Some samples cannot be ultramicrotomed because of their physical properties.
Output: Standard TEM grids with ultrathin sections of the samples, ready to be imaged by a transmission electron microscope.
CryoTEM
CryoTEM use
Cryofixation is an add-on for transmission electron microscopy, suitable for the fixation of nano-objects or near-nano-objects that depend on water as a structural component, such as liposomes. They are thereby kept hydrated without chemical fixatives, dehydration, embedding, or ultramicrotopy). Furthermore, cryofixation can image nanoparticles in a hydrated state, i.e., in a condition preceding the occurrence of drying effects that can lead to aggregation. It is not suitable for the observation of entire cells. Note: single particle reconstruction, which involves 3D reconstruction at subnanometer resolution of proteins, is not included in our service portfolio.
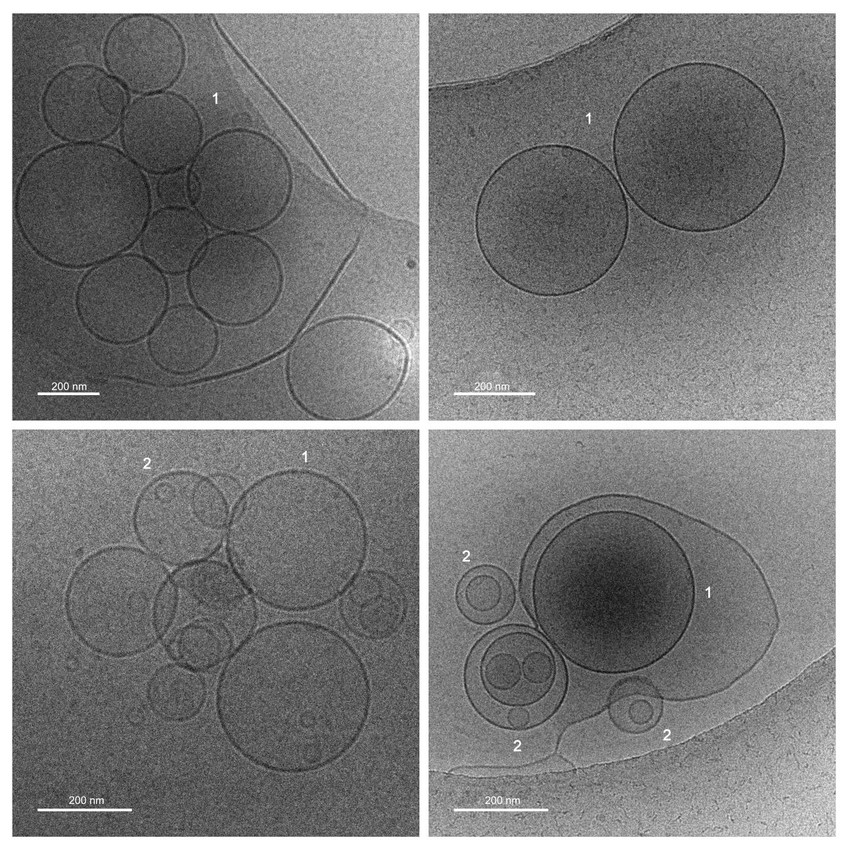
Modus operandi
Cryofixation is always performed in conjunction with transmission electron microscopy (then operating at about -170°C), and booking the TEM is mandatory to book the cryofixation equipment. Cryofixed samples are not stored longer than a few hours.
SNSF-eligible cost breakdown
CryoTEM usage includes the use of the TEM, the Leica GP2 cryo-plunger, the Gatan 626 cryo-holder and all its accessories (the pumping system, the transfer station, the heating controller), and the cryogens (liquid nitrogen and liquid ethane). The user must obtain their own cryoTEM grids. Further information see Rates.
| CryoTEM | |
| Scientific support (TEM) | 25.26 CHF/h |
| Consumables | 8.44 CHF/h |
| – Cryogen (Ethane, LN2) | 6.70 CHF/h |
| – LaB6 Gun | 2.04 CHF/h |
Summary and output
Summary: a one-hour use of the TEM for cryo (including access to all the tools for cryofixation and cryo-TEM imaging) is charged at 33.70 CHF/h.
Output: cryo-micrographs of your nanoparticles or liposomes
CryoTEM training
The training to perform cryofixation and cryo-TEM imaging is much more time-intensive than conventional TEM: a motivated participant may be able to learn cryo-TEM in about 25 hours over a period of 5-6 weeks, provided he/she brings proficiency in TEM. Training is conducted in small groups of no more than three participants. Note that grids are included in the training as cryo-TEM grids are different from conventional TEM grids. The correct type and supplier are discussed during the training.
Prerequisite
proficiency in TEM, i.e. having passed the conventional TEM training and an additional 10-20 hours experience operating the TEM without help. Showcase your experience to the admin before enrolling in the cryoTEM training.
SNSF-eligible cost breakdown
| Hourly use | Total | Total costs | |
| Scientific support | 83 CHF/h | 25 h | 2075 CHF |
| Instrument costs (cryo) | 33.70 CHF/h | 25 h | 842.50 CHF |
| CryoTEM grids | 5 CHF/piece | 25 pieces | 175 CHF |
Summary and output
Summary: Total costs for training: 3092.5 CHF. Total costs for a median group (2 people): 1546 CHF per person. Note: suitable samples, a contract longer than 1 year, and sufficient motivation are prerequisites for entering cryo-TEM training.
Output: the knowhow and handling of all the equipment to cryofix biological samples (or nanoparticle solutions in water) and the knowhow to image them.
